Introduction
Onboarding and induction processes are crucial for integrating new members into any professional team, particularly in specialised and complex fields like oncology health research. This abstract highlight the creation of a digital induction guide designed to facilitate a smoother transition for new members joining an oncology research team within the National Health Service (NHS). The emphasis on technology-driven solutions reflects the broader trend in healthcare towards digitisation and the use of innovative tools to enhance educational and training processes.
Background
Working in oncology health research presents unique challenges and opportunities. The field is characterised by its dynamic nature, with ongoing advancements in cancer treatment and research methodologies. New team members that join an oncology research team often face a steep learning curve, not only in understanding the scientific and clinical aspects of oncology but also in navigating the organisational structure and workflows of their new environment. Recognising these challenges, the need for a structured and effective induction system became apparent. Feedback from previous team members indicated that a cohesive onboarding/induction process could significantly enhance their integration into the team and their overall job satisfaction. This feedback served as a catalyst for the development of the induction guide described in this abstract.
Methods
The creation of the induction guide involved several key steps, each aimed at maximising the effectiveness of the resource:
1. Platform Selection
A digital platform was chosen to host the guide, allowing for interactive elements such as videos and hyperlinks to external resources. This decision was driven by the need to engage users more effectively than traditional paper-based guides, which can often be dull and difficult to navigate.
2. Content Development
The content of the guide was carefully curated from credible sources to ensure accuracy and relevance. Given the complexity of oncology research, the information was structured to be easily digestible, with complex concepts broken down into simpler segments using animations and other visual aids.
3. Design and User Experience
A significant emphasis was placed on the design of the guide to make it visually appealing and user-friendly. Vibrant colours and an intuitive layout were employed to capture and maintain the reader’s interest. The guide’s format was optimised for mobile devices, enabling users to access it on the go.
4. Feedback Mechanisms
To ensure the guide remains relevant and effective, a feedback loop was established. Readers are encouraged to provide anonymous feedback via a brief survey, which is used to continuously refine and update the content.
5. Sustainability and Accessibility
The guide was designed in an electronic format to minimise environmental impact by reducing the need for printed materials. Additionally, the digital format allows for easy updates as new information becomes available. A QR code was also implemented to facilitate easy access to the guide.
Results
The implementation of the induction guide has yielded positive results across several dimensions:
1. Seamless Integration
The guide has significantly improved the integration of new members into the oncology research team. By introducing the guide during the first week of induction, it lays a solid foundation for ongoing learning and professional development.
2. Enhanced Accessibility
The guide’s digital format ensures that it is easily accessible to all team members, regardless of their location. Users can quickly revisit the guide on their handheld devices whenever needed, making it a convenient and reliable resource. A quiz game was also added to aid users to assess their knowledge whilst adding a competitive component to make it enjoyable.
3. Positive User Feedback
Feedback from users has been overwhelmingly positive. The interactive and colourful nature of the guide has been particularly appreciated, with many users noting that it makes the learning process more enjoyable and less intimidating.
4. Multipurpose Tool
In addition to its primary function as an induction guide, the resource has also been repurposed as an educational tool for ongoing research activities. This dual functionality enhances its value to the team and underscores the versatility of digital resources in healthcare education.
5. Continuous Improvement
The feedback mechanism embedded in the guide has proven to be an effective tool for continuous improvement. By regularly collecting and analysing user feedback, the team can make informed decisions about updates and enhancements to the guide. How did you find this guide (Figures 1 and 2).
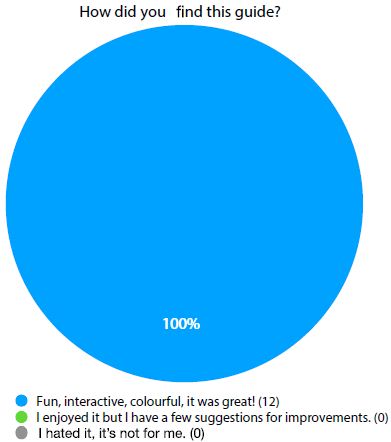
Figure 1: How did you find this guide?
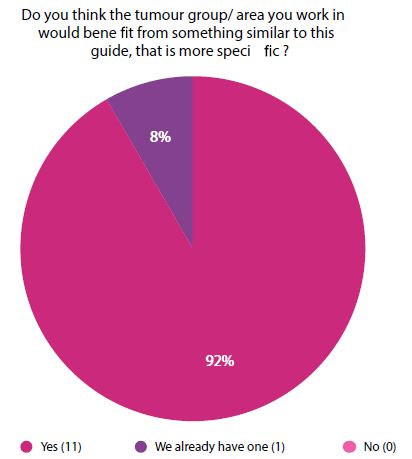
Figure 2: Do you think the tumour group/area you work in would benefit from something similar to this guide, that is more specific?
Discussion
The success of the induction guide reflects broader trends in healthcare and education, where digital tools are increasingly being used to enhance learning and training processes. The use of technology in this context offers several advantages over traditional methods:
1. Interactivity and Engagement
Digital platforms allow for the incorporation of interactive elements that can significantly increase user engagement. Videos, animations, and hyperlinks to external resources provide a richer learning experience compared to static text.
2. Flexibility and Accessibility
The ability to access educational resources on mobile devices is a key advantage in today’s fast-paced work environments. This flexibility allows team members to learn at their own pace and revisit material as needed, which can be particularly beneficial in a field as complex as oncology research.
3. Sustainability
The move towards digital resources aligns with broader sustainability goals by reducing the reliance on printed materials. This not only minimises waste but also allows for the easy updating of content, ensuring that the information remains current and relevant.
4. Feedback and Adaptation
The integration of feedback mechanisms into digital resources enables continuous improvement. By regularly updating the guide based on user feedback, the resource remains relevant and effective over time, ensuring that it meets the evolving needs of the team.
5. Cost-Effectiveness
While there may be initial costs associated with the development of digital resources, these are often offset by the long-term savings achieved through reduced printing costs and the ability to easily update content without the need for reprinting (Table 1).
Table 1: Feedback survey results
|
Date |
Do you have any suggestions for improvements? |
| 29/08/2023 | |
| 29/08/2023 | It was very explanatory and captured everything one needs to know about beginning research |
| 29/08/2023 | Great slideshow and very detailed, definitely provides a holistic overview of working in research, thank you for taking the time to make this resource! |
| 29/08/2023 | Just a correction on a name but other than that, it was great. |
| 29/08/2023 | |
| 29/08/2023 | |
| 29/08/2023 | |
| 01/11/2023 | nil |
| 24/01/2024 | no |
| 02/02/2024 | Perfect |
| 12/03/2024 | |
| 15/07/2024 | I thoroughly enjoyed the presentation! It provided valuable insights into the team and gave an overview of clinical trials. I also appreciated and was interested at the end where current trials conducted at RFH were outlined. The slides were very easy to follow and also were designed nicely. o suggestion for improvements! |
Conclusion
The development and implementation of a digital induction guide for new members of an oncology research team based in a NHS trust has proven to be a highly effective strategy for improving the onboarding/induction process. The guide’s interactive, accessible, and user-friendly design has been well-received by users, who have praised its ability to make the learning process more engaging and less daunting. Moreover, the guide’s utility extends beyond its initial purpose, serving as an ongoing educational resource for the entire team. This multipurpose functionality underscores the value of investing in digital resources for healthcare education. As the field of oncology research continues to evolve, the need for effective training resources will only grow. The success of this induction guide demonstrates the potential of digital tools to meet this need, providing a model that can be adapted and applied in other areas of healthcare and beyond.
Future Directions
Looking ahead, there are several potential areas for further development and improvement of the induction guide:
1. Expansion of Content
As oncology research continues to advance, there will be a need to regularly update and expand the content of the guide. This could include new sections on emerging research areas, advanced treatment modalities, and updates on clinical trial protocols.
2. Integration with Other Training Resources
The guide could be integrated with other training resources, such as online courses, webinars, and virtual simulations, to provide a 29/08/2023 01/11/2023 nil 24/01/2024 no 02/02/2024 Perfect 12/03/2024 15/07/2024 I thoroughly enjoyed the presentation! It provided valuable insights into the team and gave an overview of clinical trials. I also appreciated and was interested at the end where current trials conducted at RFH were outlined. The slides were very easy to follow and also were designed nicely. o suggestion for improvements! Do you have any suggestions for improvements? Date more comprehensive educational experience. This could help to reinforce key concepts and provide opportunities for hands-on learning in a virtual environment.
3. Customisation for Different Roles
While the current guide is designed for a general audience, there may be value in creating customised versions for different roles within the oncology research team. For example, separate guides could be developed for clinical researchers, laboratory technicians, and administrative staff, each tailored to the specific needs and responsibilities of these roles.
4. Data Analytics
By leveraging data analytics, the team could gain deeper insights into how the guide is being used and identify areas for improvement. For example, data on which sections are most frequently accessed, or where users tend to spend the most time, could inform decisions about content updates and enhancements.
Broader Implications
The success of this digital induction guide has broader implications for the use of technology in healthcare education and training. As the healthcare landscape continues to evolve, there will be an increasing need for innovative solutions that can keep pace with the rapid advancements in medical knowledge and practice. Digital resources, such as the induction guide described in this abstract, offer a promising way to meet this need. By providing flexible, accessible, and engaging learning experiences, these tools can help to ensure that healthcare professionals are well-equipped to navigate the complexities of their roles and contribute to the ongoing advancement of their fields. Moreover, the principles underlying the development of this guide—such as the importance of interactivity, user feedback, and sustainability—can be applied to other areas of healthcare education. Whether in medical schools, clinical training programs, or continuing professional development courses, the use of digital tools has the potential to transform the way healthcare professionals learn and develop their skills.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the digital induction guide developed for the oncology research team represents a significant step forward in the use of technology to enhance healthcare education. By leveraging the power of digital platforms, the guide provides a user-friendly, engaging, and effective resource for new team members, helping to facilitate their integration into the team and supporting their ongoing professional development. As healthcare continues to embrace digital transformation, resources like this induction guide will play an increasingly important role in ensuring that professionals are well-prepared to meet the challenges of their roles. The success of this project serves as a testament to the value of digital tools in healthcare education and offers a model that can be adapted and applied in a wide range of settings.