DOI: 10.31038/ALE.2024112
Abstract
The paper presents a four-step process for using generative AI to solve a problem, such as motivating young people to apply for a police job in a small town. Step 1 is a simulated town hall meeting to discuss the local population’s responses and issues with school safety. Step 2 is the simulated open house meeting, where AI simulates a meeting to encourage volunteering for a career in local law enforcement. Step 3 simulates four different mind- sets among potential recruits for police office and police-school officer roles. Step 4 presents a set of questions and synthesizes the four answers to each question based upon AI’s simulation of the response of each mind-set. The paper shows the power of AI to become a colleague and “knowledge worker.”
Keywords
Generative AI, Mind genomics, Police recruitment, Synthesized mind-sets
Introduction
The negative perception of law enforcement among young people is a significant factor in their decision to pursue careers in the police force. The perceived risks, challenges, and long hours can deter candidates who seek more stable and less stressful careers. This leads to fewer candidates and, in turn, to issues in meeting demands for salaries, benefits, and additional training. It should come as no surprise that the overall pool of qualified candidates may continue to shrink, making it difficult for police departments to fill vacant positions and maintain adequate staffing levels [1].
To address this issue, police chiefs should reassess recruitment strategies and identify potential barriers to attracting young people to law enforcement careers. This may involve reaching out to local schools and community organizations, offering internship programs, mentorships, and career development opportunities, and engaging young people about the benefits and opportunities of becoming a police officer [2].
To address the topic, this paper presents four strategies using generative AI as a coach and mentor. The generative AI, ChatGPT 3.5, enables the user to simulate and synthesize situations and solutions in a short time, develop insights, and then validate these insights using empirical research. As such, the paper constitutes a “vade mecum,” a guide to how one might approach this vexing problem, doing so with generative AI in a matter of 24 hours, at low cost, with the opportunity of developing critical insights about the topic along with testable suggestions.
As technology advances and automation replaces traditional jobs, the need for skilled and dedicated workers in critical roles like law enforcement becomes even more pronounced. To solve this problem, generative AI can be used to analyze and understand the underlying factors driving young people’s decisions to pursue or avoid careers in law enforcement. This data-driven approach will enable tailoring messaging, training programs, and support systems to better meet the needs and expectations of prospective candidates, ultimately increasing recruitment success.
The immediate and severe issues regarding staffing in law enforcement was brought home in an example of a town, called here TOWNX. The challenge was put forward to use a combination of generative AI and human research to address the problem. Could a system be created which could address some of the seemingly impossible-to-solve problems?
This paper presents the synthesized approach to ameliorating some of the problem, although the problem may be far from actually solvable in its entirety. Nonetheless, the structure generated here emerged with the help of generative AI (specifically ChatGPT 3.5), along with the emerging science of Mind Genomics. The paper is presented as a “work in progress,” but which can be used immediately.
The actual paper comprises four different strategies. The first two strategies deal with the reports of “meetings,” and are meant to simulate what happened, giving the reader a sense of what is going on. The second two strategies deal with mind-sets of individuals who are the likely candidates, and then questions given to these mind-sets, and how each mind-set answers the same question.
Strategy 1
The town hall meeting to discuss how the local population “came up” with answers. This strategy is based upon the book Looking Backward by author Edward Bellamy, where the forecast of what would happen in the future is written as a historical account of what had already happened.
Strategy 2
The open house meeting, where the focus was on the simulation of a meeting held to help drive volunteering to become a police officer. The vision here was to get AI to bring the reader below the surface, to discuss questions — what they really mean and how candidates might be thinking about these questions — and issues dealing with recruitment.
Strategy 3
Simulating mind-sets. The AI was told that there exist different mind-sets among the potential recruits for the police office and police-school officer roles. The AI synthesized four different possible mind-sets and provided relevant insights into the mind-sets.
Strategy 4
Creating questions about the job and then generating likely answers that each of the four simulated mind-sets would give to the same question. These are the four mind-sets used in Strategy 3. It will be the questions and answers in Strategy 3 that will be used for the empirical Mind Genomics project and reported as an accompanying paper.
Strategy 1 — A Simulated Town Meeting
A simulated town meeting with generative AI can foster creativity and innovation by providing a platform for brainstorming and idea generation. The AI can introduce new perspectives and ideas that human participants may not have considered, leading to novel solutions. Additionally, the AI can facilitate real-time collaboration and idea sharing, enabling participants to build upon each other’s thoughts and concepts. By stimulating creative thinking and encouraging out-of-the-box solutions, the simulated town meeting with generative AI can inspire innovative approaches to complex problems.
A simulated town meeting could involve a diverse group of people coming together to discuss various problems and brainstorm potential solutions. The goal is to encourage open communication, collaboration, and creativity to address complex issues facing the community. By creating a space where everyone’s opinions are heard and valued, there is the hope that innovative ideas will emerge, and practical solutions will be developed.
One potential strategy within a simulated town meeting could be to introduce generative AI that is programmed to simulate discussions about different problems and propose solutions as if they were already solved. This could help stimulate thought and generate new perspectives that human participants may not have considered on their own. The value of having AI generate solutions lies in its ability to generate ideas quickly and without bias. The AI can analyze vast amounts of data and information to offer potential solutions that may not have been considered by human participants.
However, the lack of human creativity and intuition could be a weakness of this approach. While the AI is capable of generating solutions based on existing data and knowledge, it may struggle to come up with truly innovative or groundbreaking ideas that require a high degree of creativity. Human intuition and gut instincts play a crucial role in problem-solving by guiding decision-making processes and identifying opportunities that may not be apparent through data analysis alone. By relying solely on AI-generated solutions, there is a risk of missing out on the unique insights and perspectives that human creativity can offer. Despite the potential limitations, a simulated town meeting utilizing generative AI has the potential to be a powerful tool for problem-solving. By leveraging the strengths of AI technology, such as quick data analysis and innovative idea generation, participants can benefit from a more efficient and effective problem-solving process. This approach can help foster collaboration, creativity, and diverse perspectives within the community, ultimately leading to more sustainable and impactful solutions.
Table 1 shows how the AI was prompted. Table 2 shows the summary of eight interchanges at the simulated town hall meeting.
Table 1: Prompting the AI to simulate a town hall meeting to discuss the problem.

Table 2: Part of the summarization of the town hall meeting, showing 11 different suggested topic areas, suggested by AI-created individuals assumed to have participated. The essence of the idea is shown in bold letter.


Strategy 2 — The Open House to Identify Ways to Encourage People to Volunteer
This second strategy focuses directly on using AI to provide interesting ideas to attract prospect candidates. Rather than solving a problem, as done in Strategy 1 above, the open house strategy focuses directly on the problem and how to solve it. Furthermore, this second strategy uses AI to simulate questions that would be given by the attendee, the importance of the question, as well as the motivating power of the answer. Even if the AI cannot really “dive” into the mind of the prospective candidate, the exercise itself provides a way to prepare oneself with a structured way to approach the necessary “back-and-forth” which can transform an audience member into a candidate. Table 3 shows the prompt given to the AI. Table 4 shows the AI results, comprising 14 questions along with the four answers to each question.
Table 3: Prompt given to the AI to simulate an open house devoted to recruiting.

Table 4: Results from the AI, showing 14 questions, and the four answers to each question provided by AI.
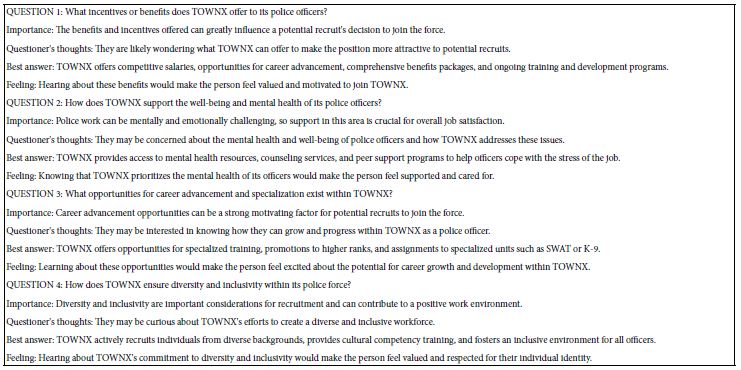
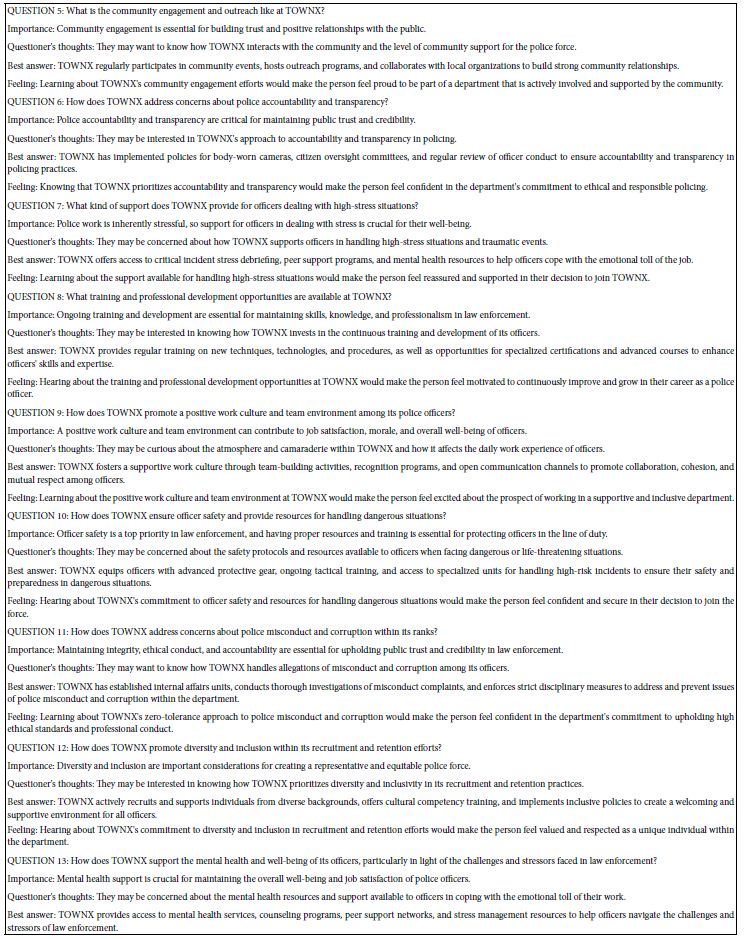

Strategy 3 — Using AI to Synthesize Mind-Sets Regarding Police Offers Specializing in School Safety
Generative AI is a powerful tool that can help companies identify the mind-sets of individuals interested in a specific job and create appealing slogans. By defining the task and asking AI to specify these mind-sets, companies can gain valuable insight into the potential target demographic for a particular job opportunity. The AI has the computational power to analyze vast amounts of data and come up with unique and innovative ideas that may not have been considered otherwise. Additionally, AI may be able to synthesize more nuanced aspects of mind-sets that are not easily quantifiable or represented in data. One potential benefit of using generative AI is that it can help companies better target their recruiting efforts by tailoring messaging to appeal to these synthesized mind-sets. The result would be more effective recruiting campaigns and ultimately result in finding the right candidates for the job. However, limitations to the effectiveness of generative AI in this context may include biases in the data used to train the AI model, which can result in inaccurate or skewed insights.
Table 5 shows the prompts given to the AI to generate mind-sets of individuals interested in a career or at least a job in school safety. Table 6 shows four mind-sets synthesized by AI for the professionalization in law enforcement and school safety.
Table 5: Prompts given to AI to generate mind-sets of individuals interested in a career or job in law enforcement and school safety.

Table 6: Four minds-sets synthesized by AI, interested in a career or least a job in law enforcement and school safety.

Strategy 4 — Have AI Generate Targeted Messaging Appropriate for Synthesized Mind-Sets and Then Test These Messages in Mind Genomics Studies with Target Age Respondents
Based on scientific principles of experimental psychology (psychophysics), statistics (experimental design, regression clustering), and consumer research (conjoint analysis), Mind Genomics ends up allowing the user to gain a deep and actionable understanding of human decision behavior, most important in the world of the everyday. Its rigorous, data-driven world view and methods provide a comprehensive analysis of the subject population for a topic, appropriate in our case for identifying key factors young individuals consider when choosing a career in law enforcement. By creating a unique profile of the target audience based on their responses to survey questions, Mind Genomics can reveal hidden patterns and trends in their thinking and decision-making processes. This helps a person or even a “chat bot” better connect with them on a personal level. In turn, the connection helps to create targeted messaging and recruitment campaigns which each alone and more strongly together, resonate with the specific needs and desires of young police officer recruits in Pennsylvania. The companion paper will show how Mind Genomics is used to evaluate the ideas generated in Strategy 4.
Strategy 4 provides a set of 21 questions, each with four answers, one answer from each mind-set. The objective of Strategy 4 is to show how a simple set of prompts (Table 7) end up creating a rich set of 21 questions and four answers to each question (Table 8). Table 8 was created in a matter of two iterations of Idea Coach in the BimiLeap. com platform, requiring less than a minute in total.
Table 7: The prompts used to create the questions and for each question four answers, one answer from each mind-set created and discussed in Table 6.

Table 8: The 21 questions created by AI, and for each question four suggested answers, one answer from each of the four mind-sets presented in Table 6.



Discussion and Conclusions
Generative AI has the potential to revolutionize the way individuals navigate their professional paths by providing creative and inventive solutions to common obstacles faced during the process of finding employment. By hosting town hall events or recruitment nights, individuals can openly discuss their professional goals and challenges, fostering a team effort to find solutions. Generative AI creates fresh perspectives which push the boundaries of conventional career paths, allowing the opportunity to explore unconventional ideas and find career paths that align with their passions and talents. Engaging in stimulating conversations with different AI-generated mind-sets can provide a diverse array of perspectives and valuable insights, broadening knowledge of different career possibilities and opening up new avenues for one’s future.
Generative AI also has the potential to completely transform the way we learn and create. Imagine a world where individuals can tap into the power of AI to generate new ideas, innovate, and discover their creative talents in ways they never thought possible. This technology opens up a whole new world of possibilities, inspiring people to think outside the box and pursue unconventional career paths previously deemed impossible.
Generative AI provides personalized learning experiences tailored to individual interests and preferences, sparking curiosity and igniting a passion for lifelong learning. Collaborating with AI to generate fresh ideas and explore new possibilities empowers people to unleash their creativity and think in innovative ways that were previously unimaginable.
In a future where generative AI is integrated into every aspect of our lives, it has the power to revolutionize the way we acquire knowledge, encouraging individuals to explore their creative side and venture into unconventional career paths. With generative AI as a guiding force, people can imagine new possibilities, dream bigger dreams, and pursue their passions with a newfound sense of purpose and excitement. One can only imagine what will emerge then, in terms of the practicalities of creating critical thinkers in school, and then having this critical thinking be part of the package one uses to create one’s job, and one’s future.
Acknowledgment
The authors would like to thank Vanessa Marie B. Arcenas and Isabelle Porat for their help in producing this manuscript.
Abbreviations
AI: Artificial Intelligence; ChatGPT: Chat Generative Pre-trained Transformer
References
- Wilson JM (2012) Articulating the dynamic police staffing challenge: An examination of Supply and Demand. Policing: An International Journal of Police Strategies & Management 35(2).
- Wilson JM and Miles-Johnson T (2024) The police staffing crisis: Evidence-based approaches Wilson JM (2012) Articulating the dynamic police staffing challenge: An examination of for building, balancing, and optimizing effective workforces. Policing: A Journal of Policy and Practice, 18.