DOI: 10.31038/CST.2022723
Abstract
Hepatocellular carcinoma prevalence rate is higher in Pakistan due to HCV mortality rate, consumption of Alchol, and regular smoking, higher level of AFP progression normal liver cells into fatty liver cells, after inflammation it convert into HCC. In this study, we find the correlation between AFP and hepatocellular carcinoma. AFP involve in development of liver cancer, LFT’s test elevation and HCV also cause of cancer.
Keywords
Hepatocellular carcinoma, Alpha fetoprotein, Alanine amino transferases, Aspartate aminotransferases
Introduction
Hepatocellular carcinoma is the 4th most common malignancy in worldwide and it is leading cause of cancer like disease in liver, and it exceed more than 1 million deaths per year by 2030 [1]. Acute hepatitis and acute liver failure are the most serious medical condition that require early diagnosis by release of IL-6, TNF-α and elevated alanine amino transferases, aspartate aminotransferases, alkaline phosphatase and α-Fetoprotein that progress healthy liver in to fatty liver known as steatosis and then inflammation occur in this and leads to hepatocellular carcinoma [2]. Most cases of HCC due to the virus like HCV and HBV, Diabetic and obesity, alcohol related diseases, non-alcohol related diseases, carcinogens like aflatoxins compounds [3]. HCC is the most common cancer that have high mortality rate in cancers due to mortality of HCV and NLFD. In Pakistan HCC ratio high due to prevalence and mortality rate of HCV [4]. The major treatment of HCC is chemotherapy, radiotherapy, transplantation and surgery. Because the most cases diagnose at the late stage, surgery cannot be performed and drugs are the only treatment of HCC [5]. Most patients in HCC become more drug resistance drug resistance. Drug treatment is the best choice of patients who are not edible for surgery. HCC is usually resistance to chemotherapeutic drugs because it hinders liver cancer treatment. In recent years targeted drugs use as medication and immune checkpoint inhibitors are introduce for treatment [6].
In the previous research evidence indicates that alpha-fetoprotein has high false-positive rate in diagnosis of early stage of HCC. The EASL clinic practices shows that AFP as a biomarker for liver transplantation and drug indicator [7]. The AFP level increased in many patients’ ad its risk for progression of HCC. AFP, currently the only biomarker available for HCC drug treatment, function as immune suppressor and promote malignancy transformation in HCC [8].
HCC is resistant to traditional chemotherapeutic agents such as doxorubicin, tetrahydrofolate, oxaliplatin, cisplatin, and gemcitabine. Currently the recommended drugs include such as targeted therapeutics and immune checkpoint inhibitors [9].
AFP is a glycoprotein that secreted by endoderm embryonic tissue. The lower level of AFP in blood due to AFP is decrease in mature hepatocytes and that AFP gene expression is blocked. It is possible that AFP involved in HCC development and progression becomes an important factor affecting HCC diagnosis and treatment. AFP plays an important role in promoting cancer cell proliferation and, inhibition cancer cell apoptosis.
LFT’s test performed for liver injury, alanine aminotransferases, aspartate aminotransferases and alkaline phosphatase. These enzymes are commonly elevated in liver disease patients. Alkaline phosphatase and AFP play important role in the diagnosis of cancer.
Case Study
The patient name was sikandar, age 56 patient feel pain in their abdomen and sudden loss of weight. The patient has already hepatitis C infection and their PCR results were positive with high viral load. Due to serious illness it admitted in emergency ward 12, Nishter Hospital Multan. The doctor panel referred some test and kept in observations for better health condition.
The total bilirubin level was 2.05 mg/dl in their blood and their normal values 0.6-1.2. The serum glutamate-pyruvate transaminase level is 43 U/L and normal values up to 40. Aspartate amino transferases and alkaline phosphatase level were high in blood respectively 151 U/L and 493 U/l show in Figure 1. It indicates liver injury and cirrhosis. The AFP test indicates correlation with Hepatocellular carcinoma. The AFP level in patient was 6101 ng/ml and normal values were 0.1 – 10. Higher level of AFP indicates that HCC have positive relation with AFP to proliferate cancer. The test formed by fully automated state of the Art analyzer Beckman Coulter 700 AIJ.
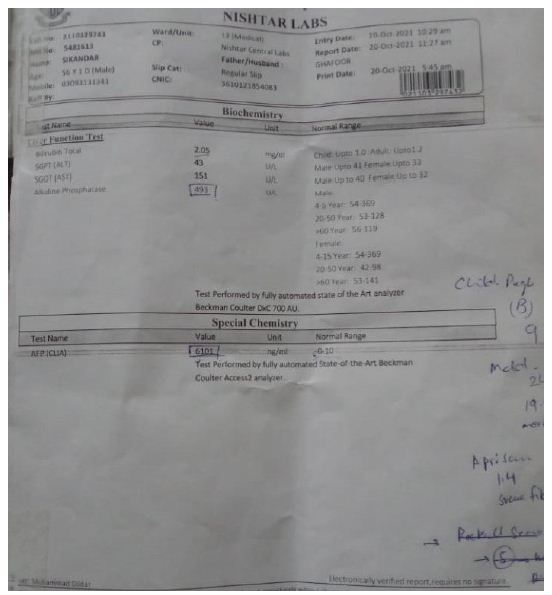
Figure 1: Liver function and Alpha Feto Protein test in patient
After blood reports, doctor suggest ultarosund Computrised Tomography whole abdominal view. In view, spleen size becomes enlarged 6 cm, calculi in gall bladder, heterogeneous patchy atrial enhancement of right lobe, and some nodules seen in both lobes of liver. The doctor finds the AFP correlation with HCC, splenomegaly, ascites, cholelithiasis and protosystematic collaterals (Figure 2).
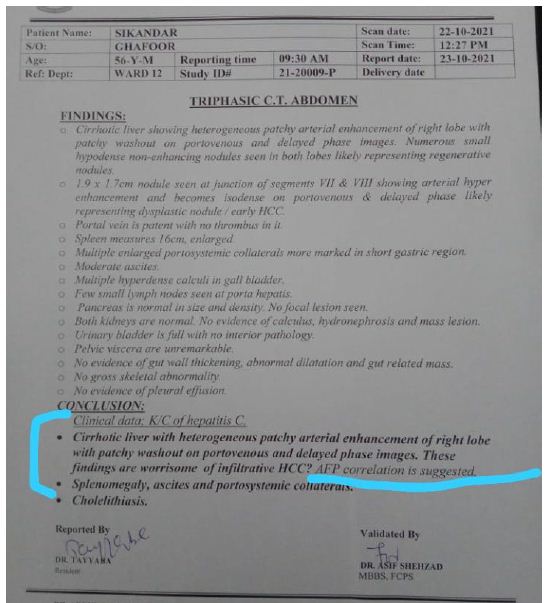
Figure 2: Ultrasound Computrised Tomography whole abdomen
The patient diagnosed with hepatocellular carcinoma at last stage, and doctor referred to liver transplantation in India. But after 4 weeks he cannot survive.
Conclusion
Hepatitis C was the major risk of hepatocellular carcinoma in Pakistan. Smoking and alcohol have big problem to influence HCC in humans. The case study shows that alpha fetoprotein has correlation with HCC. Higher Alkaline phosphatase and serum Bilirubin level enhance the liver carcinoma. AFP play role in cell proliferation, cancer cell differentiation and cell cycle arrest.
References
- Yang JD, Hainaut P, Gores GJ, Amadou A, Plymoth A, Roberts LR (2019) A global view of hepatocellular carcinoma: trends, risk, prevention and management. Nature Reviews Gastroenterology & Hepatology. 16: 589-604.[crossref]
- Effenberger M, Grander C, Grabherr F, Griesmacher A, Ploner T. et al. (2021) Systemic inflammation as fuel for acute liver injury in COVID-19. Digestive and Liver Disease. 53: 158-165.[crossref]
- Du J, Ma YY, Yu CH, Li YM (2014) Effects of pentoxifylline on nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a meta-analysis. World Journal of Gastroenterology. 20: 569.[crossref]
- Ashtari S, Pourhoseingholi MA, Sharifian A, Zali MR (2015) Hepatocellular carcinoma in Asia: Prevention strategy and planning. World Journal of Hepatology. 7: 1708. [crossref]
- Daher S, Massarwa M, Benson AA, Khoury T (2018) Current and future treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma: an updated comprehensive review. Journal of Clinical and Translational Hepatology. 6: 69.
- Liu X, Qin S (2019) Immune checkpoint inhibitors in hepatocellular carcinoma: opportunities and challenges. The Oncologist. 24: S3-S10. [crossref]
- Wong RJ, Ahmed A, Gish RG (2015) Elevated alpha-fetoprotein: differential diagnosis-hepatocellular carcinoma and other disorders. Clinics in Liver Disease. 19: 309-323. [crossref]
- Trevisani F, Garuti F, Neri A (2019) Alpha-fetoprotein for diagnosis, prognosis, and transplant selection. Seminars in Liver Disease. [crossref]
- Galluzzi L, Senovilla L, Zitvogel L, Kroemer G (2012) The secret ally: immunostimulation by anticancer drugs. Nature Reviews Drug Discovery. 11: 215-233. [crossref]