Abstract
Aim: The aim of the present study was to test whether conjugation of a synthetic peptide corresponding to a fragment of the second extracellular domain of the human serotonin 2A receptor substantially alters the in vivo pharmacodynamic blood pressure-lowering profile of the peptide in different hypertensive rat strains.
Methods: Sertuercept (SCLLADDN) was synthesized and modified using pegylation or myristolation. The two different peptide conjugates were tested in male Zucker diabetic fatty rats for acute and long-lasting blood pressure-lowering effects following single intraperitoneal administration. The myristolated Sertuercept was administered intraperitoneally to female Zucker fatty and male spontaneously hypertensive rats (SHR) and blood pressure was monitored either using tail cuff measurement (female Zucker) or by telemetry (SHR) rats. Plasma immunoglobulin G obtained by Protein G affinity chromatography in 25-week-old female Zucker or male spontaneously hypertensive rats was tested for binding to a linear synthetic peptide corresponding to the second extracellular loop of the serotonin 2A receptor. A cohort of male Zucker diabetic fatty rats was randomized to seven weeks of once-weekly myristolated Sertuercept or scrambled peptide (injections) and the kidneys were examined histologically for differences in total kidney lesions or fibrosis.
Results: Pegylated Sertuercept promoted substantial blood pressure-lowering lasting approximately 30-48 hours in male Zucker diabetic fatty rats. Blood pressure-lowering following a single injection of Myristolated Sertuercept was much longer-lasting (6-11 days) and it was effective in male Zucker diabetic fatty rats, male spontaneously hypertensive rats and in a subset of hypertensive female Zucker fatty rats. Seven weeks’ treatment with once-weekly Myristolated Sertuercept (2mg/kg) was associated with significantly fewer kidney lesions and less interstitial fibrosis compared to scrambled peptide in 25-week-old male Zucker diabetic fatty rats. Male spontaneously hypertensive rats (4 of 4 tested) harbored plasma IgG which bound significantly to serotonin 2A receptor peptide, and a subset of female Zucker fatty rats harboring IgG were responsive to blood pressure-lowering from the myristolated Sertuercept peptide.
Summary: Myristolated-Sertuercept, an epitope-specific peptide comprised of a portion of second extracellular loop of the human serotonin 2A receptor was safe, well-tolerated and effectively lowered blood pressure for one week or longer in two different strains of male hypertensive rats. These data provide proof-of-concept that once-weekly systemic drug administration is feasible to achieve not only long-lasting hypertension control, but also substantial renoprotection.
Introduction
According to the Global Epidemiology of Hypertension Study, in 2020, hypertension was the leading cause of global death and disability [1]. Hypertension prevalence is increasing worldwide, it already exceeds 1 billion affected persons, and is especially prevalent in persons living in low- and middle-income countries Although hypertension treatment and control has improved significantly in the past several decades in high-income countries, awareness and treatment/control still lag significantly in less developed parts of the world.
Hypertension is a major modifiable risk factor for cardiovascular disease (ischemic heart disease, stroke, congestive heart failure) and chronic kidney disease occurrence. One of the key factors contributing to poor hypertension control in treated patients is nonadherence to medication regimen(s). The underlying causes of nonadherence are multifactorial but include a need for higher vs. lower frequency of dosing [2]. In a recent systematic review and meta-analysis that compared once-daily vs. once-weekly dosing in the treatment of chronic diseases, once weekly dosing was associated with a 1.9-fold higher odds ratio of long-term medication adherence [3].
We previously reported on a first-in-class, novel anti-hypertensive peptide (Sertuercept) having amino acid sequence corresponding to a subregion of the second extracellular loop of the human 5-HT2A receptor [4]. The serotonin 2A receptor is normally expressed on arterial vascular smooth muscle cells where it mediates 5-HT induced arterial vasoconstriction [5]. In experiments conducted in male Zucker diabetic fatty rats (ZDF) [4], a genetic model of obese, hypertensive, type 2 diabetes, unconjugated Sertuercept had an in vivo pharmacodynamic half-life of approximately 24 hours, caused rapid, potent systolic and diastolic blood pressure-lowering (in ZDF rats) and was well-tolerated. Chronic every other daily intraperitoneal administration of Sertuercept (vs. scrambled peptide) significantly decreased renal glomerulosclerosis in male ZDF rats [4].
The aim of the present study was to test whether modification of Sertuercept via attachment of a pharmacologic carrier can extend the in vivo blood pressure-lowering effect of the peptide drug leading to a long-acting analogue that is safe, well-tolerated, efficacious and could be administered in a once-weekly chronic regimen that reduces end-organ dysfunction associated with poor, long-term hypertension control.
Animal and Methods
Animals
All procedures were conducted according to the National Institutes of Health (NIH) Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals and approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of the Veterans Affairs Medical Center (East Orange, New Jersey). Male ZDF (N=12) female Zucker fatty rats (N=21) and male spontaneously hypertensive rats (SHR) were obtained from Charles River Laboratories (Kingston, NY) at approximately 6 weeks of age. All rats were single housed upon arrival, with modest enrichment (a PVC tube). Rats were provided ad libitum access to food and water and maintained in a 12 h light/dark cycle with lights on at 0630. All procedures occurred during the light phase of the cycle.
Synthetic Peptides
Unconjugated Peptide
Synthetic peptides were synthesized at Lifetein Inc. (Hillsborough, NJ). The lyophilized peptides were aliquoted and stored (under desiccated conditions) at −40°C prior to use. On the day of intraperitoneal (IP) administration, an aliquot of lyophilized peptide was reconstituted in sterile saline at the indicated concentration.
Lyophilized peptide was stored for up to 4 weeks (at −40°C) prior to obtaining newly-synthesized peptide needed in chronic drug administration experiments.
Unconjugated Peptides
Sertuercept (Decoy Receptor Peptide)
A linear synthetic peptide, SCLLADDN, having amino acid sequence identical to that of a fragment of the second extracellular loop region of the human 5-hydroxytryptamine 2A receptor was synthesized and had ≥ 95% purity.
Scrambled Peptide Sequence LD.8
The scrambled peptide had a sequence of LASNDCLD (LD..8) and a purity of 96.37%, MW 849.91.
Conjugated Peptides
Pegylated SCLLADDN-‘Pegsertuercept’
The starting material, PEG2K-or-above DBCO is a mixture of polyethylene glycol (PEG) and the average molecular weight is 1K. The purity of the free peptide is ≥95%. The mechanism for generation of pegylated Peptide 2 is as follows: Lys(Azide)-SCLLADDN + DSPE-PEG2000 (or above)-DBCO. The click chemistry occurs between azide and DBCO. The sequence of the final product is K(DBCO-DSPE-PEG2K)-SCLLADDN. The purity is >95% and the MW is 1004.09.
Myristolated SCLLADDN or ‘Myr-Sertuercept
The synthetic SCLLADDN (Sertuercept) peptide was myristolated on the N-terminus at Lifetein Inc; it had >91% purity. It was reconstituted in sterile saline containing 10% DMSO to improve solubility prior to intraperitoneal administration in rats.
Non-survival surgery (25-weeks of age)
Rats were anesthetized with xylazine/ketamine prior to undergoing non-survival surgery during which they were perfused with 4% paraformaldehyde in PBS. The kidneys (male ZDF rats) were post-fixed for 24-48 hours in 4% paraformaldehyde and then stored in 70% ethanol at 4°C prior to shipment to Histoserve, Inc. (Germantown, MD). Kidneys were sectioned and stained with H&E and Masson’s trichrome. Blood (male SHR, female Zucker fatty rats) was obtained by cardiac puncture immediately before non-survival surgery for isolation of plasma IgG autoantibodies.
Tail-cuff Blood Pressure Monitoring
Tail cuff blood pressure measurement was performed using an automated CODA noninvasive blood pressure system (Kent Scientific, Torrington, CT) in male Zucker diabetic fatty and female Zucker fatty rats, as previously reported [4].
Telemetric Blood Pressure Monitoring
Surgical Placement of Blood Pressure Implant and Telemetry Device
Stellar telemetry, real-time implants (TSE Systems, Chesterfield, MO) were placed in the left femoral artery of three male, 16-week-old SHR rats and one 16-week-old male Sprague-Dawley rat using procedures described in the Stellar Surgical Manual (TSE Systems, Chesterfield, MO). Correct placement was verified by the blood pressure waveform. The telemetry device was placed in a subcutaneous pocket on the dorsal surface between the shoulder blades, and the device was secured to the surrounding muscle with non-absorbable suture. The rats were allowed 7 days to recover post-operatively before initiation of blood pressure data acquisition.
Real-time Blood Pressure Implant Data Acquisition
The Stellar Telemetry, real-time implants are supported in Notocord-hem software (Instem). The software was programmed to acquire blood pressure data at 20-second intervals (up to ten measurements at each timepoint) before and for up to 12 days after IP administration of Myr-Sertuercept or scrambled peptide.
Renal Histology
Comparisons between male ZDF rats randomized to 7 week’s treatment with (Myr-Sertuercept vs. scrambled peptide) were made by Dr. Jerrold M. Ward (veterinary pathologist) using Masson’s trichrome fibrosis score and total kidney lesion score. The fibrosis score ranged from 0-4, where 0: no fibrosis, 1: minimal fibrosis, 2: mild fibrosis, 3: moderate fibrosis, and 4: severe fibrosis. An individual glomerular score and an interstitial score (for the one kidney examined from each individual rat) was determined separately. Twenty-forty glomeruli were examined in each kidney, both in areas involved or not involved by interstitial fibrosis. A total kidney lesion score (from H&E sections) was based on presence (or absence) and severity of hydronephrosis, dilated tubules, glomerular and/or interstitial fibrosis. The veterinary pathologist examiner was unaware of the treatment assignment group during examination of histologic sections of rat kidneys.
Protein G affinity Chromatography
Rat plasma samples obtained in (25-week-old female Zucker fatty or male SHR) rats were subjected to Protein G affinity chromatography for isolation of IgG as previously reported [6]. Enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) for serotonin 2A receptor second extracellular loop peptide. Rat IgG specimens were tested for binding to the serotonin 2A receptor peptide corresponding to the second extracellular loop domain (QN..18) (Lifetein, Inc) in an ELISA performed as previously reported [6].
Statistical Analysis
Comparisons were made using Student’s unpaired t-test; or time series analysis.
Results
Long-lasting Blood Pressure-lowering Effect of Pegsertuercept
A single 1 mg/kg IP dose of Pegylated-Sertuercept caused statistically significant 8.9 mm Hg mean lowering in systolic blood pressure (Table 1) and a statistically significant 9.8 mm Hg mean lowering in diastolic blood pressure (Table 2) compared to 2 mg/kg scrambled Peptide 2 (P<0.01) in 12-week-old male ZDF rats. There was no significant effect of time on blood pressure-lowering effect from the two drugs (not shown in Table 1 or 2).
Table 1: Comparison of systolic blood pressure-lowering effect from Pegsertuercept (1 mg/kg) vs. scrambled peptide LD.8 (2 mg/kg) intraperitoneal injection in 12-week-old male ZDF rats.
|
Treatment |
Estimate |
SE |
DF |
t Value |
Pr>t |
|
| Effect | ||||||
| Intercept |
141.66 |
5.4602 |
5 |
25.94 |
<.0001 |
|
| Trt | PegSertuercept |
-8.9162 |
2.5229 |
38 |
-3.53 |
0.0011 |
| Trt | Scrambled Peptide |
0 |
||||
Single Pegsertuercept (1 mg/kg) IP injection caused -8.9 mm Hg reduction in mean systolic blood pressure compared to scrambled peptide (2 mg/kg IP). SE: Standard Error.
Table 2: Comparison of diastolic blood pressure lowering effect from Pegylated Sertuercept (1 mg/kg IP) vs. scrambled peptide LD..8 (2 mg/kg IP) in 12-week-old male ZDF rats.
|
Treatment |
Estimate |
SE |
DF |
t Value |
Pr>t |
|
| Effect | ||||||
| Intercept |
98.1654 |
4.376 |
5 |
22.43 |
<.0001 |
|
| Trt | PegSertuercept |
-9.7771 |
0.5121 |
40 |
-19.09 |
<.0001 |
| Trt | Scrambled Peptide |
0 |
0 |
Single Pegsertuercept (1 mg/kg) intraperitoneal (IP) injection caused mean -9.8 mm Hg reduction in mean diastolic blood pressure compared to IP injection of scrambled peptide (2 mg/kg). SE-standard error.
A single IP injection of either 1 mg/kg (shown in Figure 1) or 0.75 mg/kg pegylated Sertuercept (not shown in Figure 1) caused significant and long-lasting decline(s) in mean systolic and diastolic blood pressure in male (12-week-old) ZDF rats. The effect was sustained for at least 30 hours and less than 48 hours (Figure 1). Scrambled peptide sequence LD..8 (2 mg/kg IP) had no significant effect on systolic or diastolic blood pressure in age-matched male ZDF rats (grey line, Figure 1).
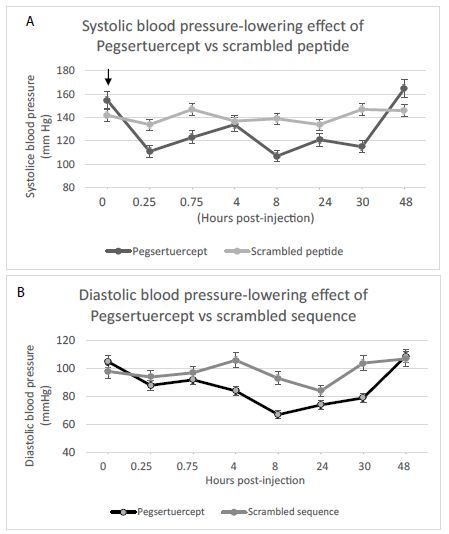
Figure 1: Single intraperitoneal dose of Pegsertuercept (1 mg/kg) (arrow) caused significantly greater systolic (A) and diastolic blood pressure-lowering (B) vs scrambled peptide (2 mg/kg) IP in 12-week-old male ZDF rats (n=4 per group). Each point is the mean ± SD.
Significantly Longer-lasting Blood Pressure-lowering Effect of Myristolated Sertuercept
A single 2 mg/kg IP dose of Myr-Sertuercept caused statistically significant 17.4 mm Hg mean systolic blood pressure-lowering and statistically significant 12.0 mm Hg mean diastolic blood pressure-lowering compared to 1 mg/kg scrambled Peptide 2 (P<0.02) (Table 3A and 3B). There was no significant effect of time on blood pressure-lowering effect from the two drugs (not shown in Table 3).
Table 3: Time series analysis of difference in systolic (A) and diastolic (B) blood pressure lowering effect after administration of single IP dose of Myr-Sertuercept vs. scrambled peptide 2 in two groups of 12-week-old male Zucker diabetic, fatty rats (N=4 rats per drug treatment group).
| A) Systolic | |||||
| Drug |
Estimate |
Standard Error |
DF |
t Value |
Pr>lti |
| Myr-Sertuercept |
-17.439 |
5.0163 |
5 |
-3.48 |
0.0177 |
| Scrambled Peptide |
0 |
||||
| B) Diastolic | |||||
| Drug |
Estimate |
Standard Error |
DF |
t Value |
Pr>lti |
| Myr-Sertuercept |
-12.0471 |
3.23 |
5 |
-3.73 |
0.0136 |
| Scrambled Peptide |
0 |
||||
Single Myr-Sertuercept (2 mg/kg) intraperitoneal (IP) injection caused mean -17.4 mm Hg reduction in mean systolic and mean -12.0 mm Hg reduction in diastolic blood pressure vs. IP scrambled peptide (2 mg/kg). The model included adjustment for difference in baseline mean blood pressure. SE-standard error.
Next, the blood pressure-lowering effect of Myr-Sertuercept at doses ranging from 1.0-2.5 mg/kg was tested (for up to nine days) following a single IP injection in male ZDF rats. Blood pressure-lowering by 1 mg/kg Myr-Sertuercept was not only rapid in onset, but substantial (Figure 2). Both younger (12-week-old) and older (25-week-old) male ZDF rats experienced similar significant blood-pressure lowering following IP injection of 2 mg/kg Myr-Sertuercept (Table 4). At doses ranging from 1.0-2.5 mg/kg, IP Myr-Sertuercept dose-dependently lowered blood pressure and the effect (at higher doses) was sustained for 7-9 days (Table 4). Myr-Sertuercept was safe and well-tolerated. None of the male ZDF rats experienced acute hypotension even at the highest dose tested. Vehicle (10% DMSO) alone or scrambled peptide in sterile saline had no discernable effect on blood pressure in age-matched male ZDF rats (data not shown).
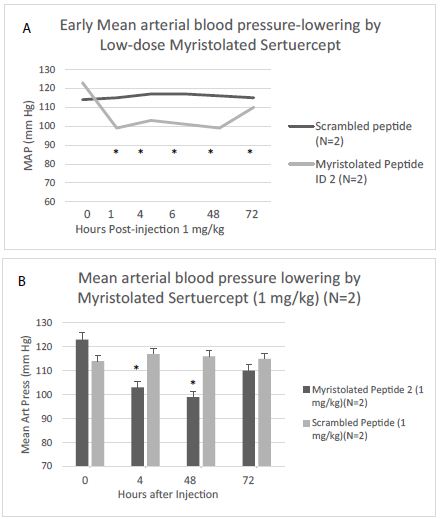
*P<0.05 compared to baseline mean arterial pressure
Figure 2: Rapid- onset and sustained blood pressure-lowering effect of low dose Myr-Sertuercept peptide following IP injection in 13-week-old male ZDF rats. Results are mean ± SEM of multiple determinations at each timepoint in each of two male ZDF rats that received either 1 mg/kg Myr-peptide or Scrambled peptide; *P<0.05 compared to baseline MAP.
Table 4: Change in Blood pressure in response to IP administration of scrambled (LN..8) or Myr-Sertuercept: each at 2 mg/kg in 25-week-old male Zucker diabetic fatty rats.
| Peptide |
Day 0 |
Day 2 |
Day 5 |
Day 7 |
| Systolic | ||||
| Scrambled (LN..8) (N=3 rats) |
140 ± 6 |
148 ± 1 |
147 ± 10 |
151 ± 12 |
| Myr-Peptide 2 (N=5 rats) |
144 ± 9 |
121 ± 7** |
125 ± 12* |
134 ± 9 |
| Diastolic | ||||
| Scrambled (LN..8) (N=3 rats) |
95 ± 10 |
94 ± 7 |
101 ± 8 |
105 ± 7 |
| Myr-Peptide 2 (N=5 rats) |
103 ± 6 |
77 ± 4** |
82 ± 10* |
92 ± 7* |
Results are mean ± SD; **P<0.01 vs. day 0; *P<0.05 vs. day 0.
Male SHR Rats
The spontaneously hypertensive rat (SHR) is an inbred strain derived from Wister-Kyoto rats selected for successive matings based on having spontaneously-occurring hypertension. The SHR rat is a recognized model of essential hypertension that is neither obese nor diabetic. Unlike male ZDF rats, male SHR rats do not develop early, moderate-severe proteinuric nephropathy [7], however, they are known to exhibit certain cell-mediated and humoral immunologic defects [8] including harboring autoantibodies to several unknown vascular antigens [9]. Myr-Sertuercept (2.0 mg/kg IP) had little or no significant blood pressure-lowering effect in three SHR rats. Myr-Sertuercept (5.0-10.0 mg/kg IP) dose-dependently lowered blood pressure, and the effect was long-lasting (up to 9-11 days) at the 7.5 or 10.0 mg/kg dose, respectively (Figure 3, Tables 5 and 6). Myr-Sertuercept was safe and well-tolerated; none of the rats experienced any untoward effect (e.g. acute hypotension) after single-or repeated dose administration over a four-week testing period. A single normotensive male SD rat (monitored telemetrically) did not experience any significant blood pressure-lowering (or adverse effect) at any dose of Myr-Sertuercept tested including the highest (10 mg/kg) dose. Vehicle (10% DMSO) or scrambled peptide (in sterile saline) had no discernable effect on blood pressure in age-matched male SHR rats (data not shown).
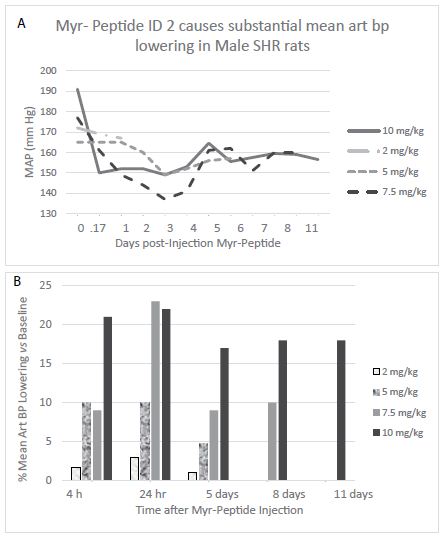
Each (time)point represents the mean of five-ten telemetric determinations (Stellar implant, TSE Systems Inc) having standard error of approximately 1%.
Mean MAP-lowering (%) at the indicated timepoint compared to baseline MAP
Figure 3: Dose-dependence and sustained blood pressure- lowering effect of Myr-Sertuercept in twenty-week old male SHR rats.
Table 5: Summary of dose-dependence and durability of mean arterial blood pressure-lowering following single IP administration of myristolated Sertuercept at indicated doses Myristolated.
|
Myristolated Sertuercept Dose |
Acute Peak blood pressure-lowering (%) |
Duration of Action (days) |
|
Mean arterial BP |
||
| 1 mg/kg |
6-8% |
4-6 |
| 1.5 mg/kg |
14% |
7 |
| 2.0 mg/kg |
14-22% |
3; 7 |
| 2.5 mg/kg |
19-30% |
9 |
Results represent average of treatment in two, 11-13-week-old male ZDF rats at each specific dose
Table 6: Summary of dose-dependence and durability of mean arterial blood pressure-lowering effects after single IP administration of myristolated Sertuercept in 25-week-old male SHR rats.
|
Myristolated Peptide 2 Dose |
Acute Peak blood pressure-lowering (%) |
Duration of Action (days) |
|
Mean arterial BP |
||
| 2.0 mg/kg |
1-3% |
5 |
| 5.0 mg/kg |
5-10% |
5 |
| 7.5 mg/kg |
9-23% |
8 |
| 10.0 mg/kg |
17-22% |
11 |
Results represent average of treatment in three male SHR rats at each specific dose
Female Zucker Fatty Rats
Unlike their male counterparts, female Zucker fatty rats do not develop diabetes mellitus on the same diet fed to male ZDF rats; female ZDF rats exhibit a much milder form of hypertension and proteinuria is mild. A single IP injection of Myr-Sertuercept (2 mg/kg) caused rapid significant systolic and diastolic blood pressure-lowering in approximately 60% (12/21) of female Zucker fatty rats tested at 24-hour after drug administration. The magnitude and time course of blood pressure change in representative ‘responder’ and ‘non-responder’ female Zucker rats following a single 2 mg/kg IP dose of Myr-Sertuercept is shown in Figure 4. Mean arterial blood pressure-lowering was substantial (23-27%) 1-3 days after Myr-Sertuercept (2 mg/kg) in a ‘responder’ female Zucker fatty rat (Figure 4). Blood pressure-lowering was sustained for up to 6 days in this and other female Zucker rat responders (not shown). There was no effect of scrambled peptide (2 mg/kg) following IP injection in three female Zucker fatty rats tested (data not shown).
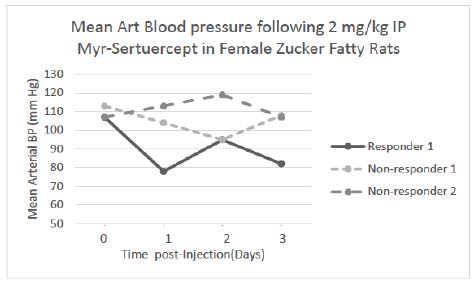
Each point is the average of three of more determinations which varied by <15%
Figure 4: Mean arterial blood pressure-lowering following a single 2 mg/kg IP dose of Myr-Sertuercept in three representative ‘responder’ and ‘non-responder’ 20-week-old female Zucker fatty rats. Results are the mean of three or more determinations which varied by < 15%.
Reno-protection from Chronic, Once-weekly Treatment with Myr-Sertuercept for Seven Weeks
Chronic once-weekly IP administration of Myr-Sertuercept (vs. scrambled peptide) (each at 2 mg/kg concentration) for seven weeks was associated with significantly lower renal interstitial collagen score (P<0.02) and total kidney lesion score (P<0.003) (N=14 male ZDF rats, Figure 5). Kidneys from rats treated with scrambled peptide not only had significantly more interstitial fibrosis (vs kidney from Myr-Sertuercept-treated rats), but the areas of fibrosis were larger than in Myr-Sertuercept-treated rats. Rats randomized to Myr-Sertuercept vs. scrambled peptide did not differ significantly in their baseline body weight or plasma glucose concentration prior to initiation of treatment (data not shown).
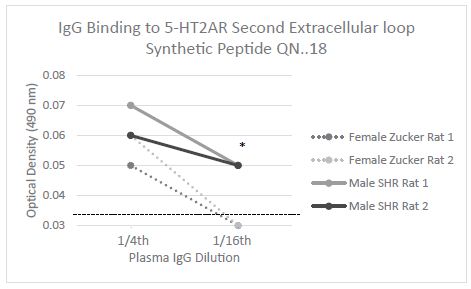
*P<0.05, mean OD in IgG from two male SHR rats vs. two female Zucker fatty rats Dashed line is the background optical density (0.032 absorbance units).
Figure 5: Level and titer of Rat IgG binding to synthetic peptide QN.18 identical to the second extracellular loop of the serotonin 2A receptor.
Serotonin 2A Receptor Plasma IgG Autoantibodies in Different Rat Strains
We next tested plasma IgG from male SHR rats (n=4) and female Zucker fatty rats (N=7) for binding to a synthetic peptide identical to the second extracellular loop of the serotonin 2AR receptor. In a prior study, male ZDF rats harbored IgG autoantibodies that displayed significant binding to the 5-HT2AR, second extracellular loop peptide, QN…18 [6]. Here, we report that IgG in all four of four male SHR rats tested displayed significant binding to the 5-HT2AR peptide, but IgG in only 2 of 7 female Zucker fatty rats tested displayed increased binding to the 5-HT2AR peptide (data not shown). Plasma IgG binding to the serotonin 2A receptor second extracellular loop peptide was significantly increased (P<0.05) in the IgG from male SHR rats (n=2) compared to female Zucker fatty rats (n=2) (Figure 6). The female Zucker rat having plasma IgG which exhibited relatively higher binding in the 5-HT2AR ELISA also had a robust blood pressure-lowering response to Myr-Sertuercept (data not shown in Figure 6).
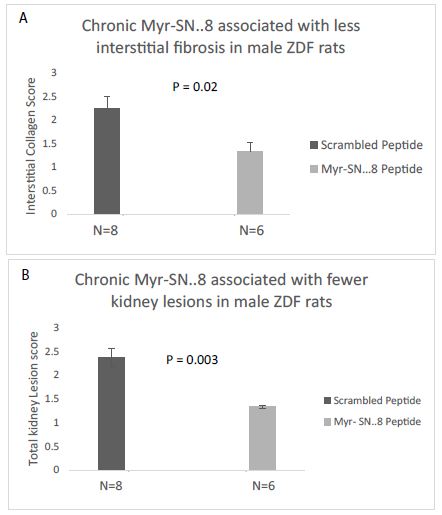
Figure 6: Chronic (7-week) once weekly IP administration of Myr-Sertuercept (2 mg/kg) significantly reduced A) renal interstitial collagen score and B) total lesions compared to identical dose and course of scrambled peptide in 16-23-week-old male ZDF rats. Results are mean ± SD.
Safety
There were few if any acute or chronic side effects from Myr-Sertuercept administered IP at doses ranging from 1-10 mg/kg in male ZDF (N=16), female ZDF (N=21) or male SHR rats (N=10). Two male Zucker diabetic fatty rats who were severely hyperglycemic (capillary glucose >500 mg/dL) developed a syndrome of inability to gain weight and failure to thrive. Both rats had been randomized to seven weeks’ treatment of once weekly Myr-Sertuercept and died at approximately 20-22 weeks of age. A limited necropsy performed in one of the rats revealed severe diabetic gastroparesis, a known complication in the hyperglycemic rodent [10].
Discussion
Two different conjugated forms of the synthetic peptide SCLLADDN (Sertuercept) substantially lowered systolic and diastolic blood pressure in male Zucker diabetic fatty rats. Blood pressure lowering following IP administration of Peg-sertuercept (2 mg/kg) was sustained for ~ 30 hours consistent with the known effect of pegylation on prolonging circulation time and decreasing proteolytic degradation in other modified proteins [11]. Myristolation of Sertuercept (SCLLADDN) on the amino terminus led to an even longer duration of blood pressure-lowering ranging from 6-11 days or longer depending on the strain and dose administered. This is consistent with enhanced lipid solubility and perhaps slower release into the circulation of myristolated vs. pegylated proteins.
Most FDA-approved medications to treat essential hypertension are available for oral administration. However, owing to their relatively short half-lives in vivo, even the most potent classes of oral anti-hypertensive medication require once or twice daily dosing. Presently, there is no FDA-approved class of anti-hypertensive medication whose duration of action extends substantially beyond 24 hours following a single (oral) dose. According to the World Health Organization, approximated 26-29% of the world population suffers with hypertension [1]. Hypertension is the single leading risk factor for global death and disability. Roughly one-half of treated hypertensive patients do not reach their target desirable blood pressure goal in part because of the need to take more than one medication at (daily) or more frequent intervals. Patient nonadherence to anti-hypertensive medication use is the leading cause of residual morbidity and mortality due to hypertension [2]. It could be substantially reduced through the advent of a potent, long-lasting blood pressure-lowering medication requiring only once-weekly self-administration.
The present data suggest that myristolated Sertuercept (Myr-Sertuercept) is a first-in-class, anti-hypertensive medication which meets the goal of safety and efficacy in a once-weekly formulation that can be self-administered. Once weekly Myr-Sertuercept not only provided long-lasting blood pressure control, but a short 7-week course of (once-weekly) injections significantly reduced the incidence of renal interstitial fibrosis and all kidney lesions in the male Zucker diabetic fatty compared to age-matched ZDF rats treated with scrambled peptide. These data are in agreement with an earlier report that alternate daily administration of unconjugated Sertuercept peptide (for ten weeks) significantly reduced glomerular fibrosis in the male ZDF rat compared to ZDF rats treated with scrambled peptide [4].
Male SHR rats suffer with a severe form of hypertension, and they required 3-5 fold higher concentration of Myr-Sertuercept (IP) to promote substantial blood pressure-lowering compared to male ZDF rats. On the other hand, not all female Zucker fatty rats (which generally exhibit a milder form of hypertension compared to male ZDF rats) experienced significant blood pressure-lowering in response to Myr-Sertuercept. Differences in endothelial injury, and endothelial nitric oxide synthase expression between male and female Zucker rats may account in part for the observed sex difference. For example, estrogen is known to augment endothelial nitric oxide synthase important in mediating vasodilation (Figure 7) [12].
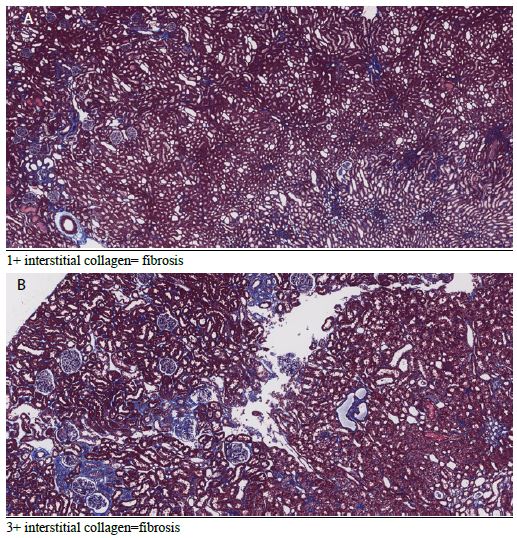
Figure 7: Representative Masson’s trichome-stained kidney section from male ZDF rat treated with either (A) Myr-Sertuercept or (B) scrambled peptide (2 mg/kg) for seven weeks.
Another contributory factor may be reduced level of plasma serotonin 2A receptor IgG in female Zucker compared to either male SHR or male ZDF rat. Our in vitro studies suggested that Sertuercept may interfere with the ability of agonist serotonin 2A receptor IgG autoantibodies to bind and activate the serotonin 2A receptor [4]. Sertuercept was designed as a structural mimic of the sub-region of the second extracellular loop of the 5-HT2A receptor most avidly targeted by ZDF rat and human pathologies IgG autoantibodies [13]. Male SHR and ZDF rat IgG not only bound to a serotonin 2A receptor peptide fragment, but the male ZDF rat IgG [6] and human pathologies’ IgG harbored endothelial cell toxicity in vitro that could be prevented by treatment with highly selective 5-HT2A receptor antagonists [14].
In summary, myristolation of Sertuercept on the amino terminus led to a novel long-lasting, safe and effective ‘first-in-class’ drug which potently lowered blood pressure in male Zucker fatty rats, and in male spontaneously hypertensive rats and substantially prevented renal interstitial fibrosis in male ZDF rats. Myr-Sertuercept may be a game-changing, once-weekly, anti-hypertensive, renoprotective medication particularly well-suited to address the problem of poor long-term medication adherence in patients on complex regimens.
References
- Mills KT, Stefanescu A, He J (2020) The global epidemiology of hypertension. Nat Rev Nephrol 16: 223-237. [crossref]
- Moise N, Schwartz J, Bring R, Shimbo D, Kronish IM (2015) Antihypertensive drug class and adherence: an electronic monitoring study. American Journal of Hypertension 28(6): 717-721. [crossref]
- Iglay K, Cao X, Mavros P, Joshi K, Yu S, et al. (2015) Systematic Literature Review and Meta-analysis of Medication Adherence With Once-weekly Versus Once-daily Therapy. Clin Ther 37(8): 1813-1821. [crossref]
- Zimering MB (2021) A Serotonin 2A-Receptor Decoy Peptide Potently Lowers Blood Pressure in Male Zucker Diabetic, Fatty, Hypertensive Rats. Endocrinol Diabetes Metab J 5(2). [crossref]
- Watts SW, Morrison SF, Davis RP (2012) Barman SM Serotonin and blood pressure regulation. Pharmacol Rev 64(2): 359-388. [crossref]
- Zimering MB, Grinberg M, Burton J, Pang K (2020) Circulating Agonist Autoantibody to 5-Hydroxytryptamine 2A Receptor in Lean and Diabetic Fatty Zucker Rat Strains. Endocrinol Diabetes Metab J 4(3): 413. [crossref]
- Feld LG, Van Liew JB, Brentjens JR, Boylan JW (1981) Renal lesions and proteinuria in the spontaneously hypertensive rat made normotensive by treatment. Kidney Int 20(5): 606-614. [crossref]
- Kim JY, Lee E, Koo S, Kim CW, Kim I (2021) Transfer of Th17 from Adult Spontaneous Hypertensive Rats Accelerates Development of Hypertension in Juvenile Spontaneous Hypertensive Rats. Biomed Res Int. [crossref]
- Ofosu-Appiah W, Huang LY, Kuhnle M, Sfeir G, Kennel A (1996) Autoantibodies against arterial antigens: characterization by ELISA and immunoblot analysis in the spontaneously hypertensive rat. Clin Exp Hypertens 18(1): 21-35. [crossref]
- Chang FY, Lee SD, Yeh GH, Wang PS (1996) Influence of blood glucose levels on rat liquid gastric emptying. Dig Dis Sci 41(3): 528-532. [crossref]
- Veronese FM, Mero A (2008) The impact of PEGylation on biological therapies. BioDrugs 22(5): 315-329. [crossref]
- Lekontseva O, Chakrabarti S, Jiang Y, Cheung CC, Davidge ST (2011) Role of neuronal nitric-oxide synthase in estrogen-induced relaxation in rat resistance arteries. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 339(2): 367-375. [crossref]
- Zimering MB (2019) Autoantibodies in Type-2 Diabetes having Neurovascular Complications Bind to the Second Extracellular Loop of the 5-Hydroxytryptamine 2A Receptor. Endocrinol Diabetes Metab J 3(4): 118. [crossref]
- Zimering MB (2018) Circulating Neurotoxic 5-HT2A Receptor Agonist Autoantibodies in Adult Type 2 Diabetes with Parkinson’s Disease. J Endocrinol Diabetes 5(2). [crossref]