Abstract
AI (Chat GPT3.5) embedded in the Mind Genomics platform (Idea Coach feature of BimiLeap.com), was used to synthesize a teaching approach for critical thinking. The exercise, strictly based on interaction with AI, was guided by the request of students in the Gymnasium of Novi Sad, Serbia, to create a tool which would allow them to experience critical thinking in a gamified manner. The process and prompts are presented in this paper, with the path to create a new game, Eco-Serbia. The paper shows how to introduce the topic, the power of AI to simulate discussions about a topic, to create the specifics for the game, and then shows additional analyses. These additional analyses, done after the project has been ‘closed’ by the user. include showing how to discover key ideas, themes, perspectives, and types of responses by different audiences. The paper finishes with a detailed opportunity analysis of four innovations about eco-Serbi as suggested by the AI [1-4].
Introduction
Teaching gymnasium-level students critical thinking is vital; it empowers them to analyze information, evaluate arguments, and reach informed conclusions. Developing critical thinking skills enables students to sharpen their awareness of the world around them, prompting them to question assumptions, form their own opinions, and approach challenges with innovative solutions. The result is enhanced academic achievements while being equipped with the skills to navigate complex challenges in a diverse and interconnected world [5-9].
Integrating critical thinking into the high school gymnasium curriculum ignites student creativity, inspiring them to generate innovative ideas and solutions. Through the application of critical thinking skills across subjects such as science, literature, and history, students increase their understanding, interact meaningfully with the material, and enjoy a sense of curiosity and intellectual exploration. This method boosts academic success while igniting a lasting love for learning, inspiring students to engage in critical thinking across all areas of their lives.
Gamifying Strategy: Create a Game About the Topic, One Requiring and Rewarding Critical Thinking
Gamifying by using AI to create a game for eco-tourism in Serbia adds a level of excitement and engagement for the students. By turning the process into a game, it becomes more interactive and enjoyable, making the learning experience more fun and memorable. The outcome of making the AI effort focused on gamifying the project is more motivated students, enthusiastic about the task at hand. They will be more likely to invest their time and creativity into the project, leading to a higher quality final product [10-13].
When our Serbian gymnasium students in Novi Sad use AI and Mind Genomics-based thinking to create a game for eco-tourism in Serbia, we expect them to feel a sense of accomplishment and pride in their work. They will likely be more excited and engaged in the project, as they see it as a fun challenge rather than a tedious academic task. By gamifying the effort, they will be more likely to collaborate with their peers, think outside the box, and push themselves to create something unique and innovative [14-17].
By using AI to transform the creation of the eco-tourism game for Serbia into a gamification project, we hope to foster creativity, critical thinking, and a passion for innovation among our students. This approach will not only make the learning process more enjoyable and engaging but also equip them with valuable skills and experiences to apply in their future endeavors.
The remainder of this paper shows the approach, done virtually all with the aid of generative AI, specific Chat GPT3.5, using the Mind Genomics platform (www.BimiLeap.com). The AI is available through the Idea Coach feature. The set-up portions of the program are done by prompts easily created by the user. The detailed analysis after the program is closed, is done by a set of embedded prompts in the BimiLeap. Program and returns automatically for each iteration after the project is closed. The results done here required about 90 minutes. The deeper analysis was returned after the AI had finished its deeper analysis.
Phase 1 – ‘Listening in on the Conversations Among 10 Students When They Hear About the Project
Observing a conversation from the sidelines offers a glimpse into the thoughts, emotions, and viewpoints of individuals regarding a specific subject. The genuine voices of individuals discussing a topic offer an authenticity that written sources often lack. The subtleties of tone, body language, and emotions in spoken conversations enrich the understanding of the topic at hand.
Engaging in conversations about a topic fosters a deeper connection and understanding that reading from a textbook or article simply cannot achieve. Hearing firsthand accounts and personal anecdotes allows us to connect more deeply with the topic, revealing its significance in our own lives. Conversation’s human element weaves empathy and understanding into the fabric of discourse, essential for unraveling the complexities of any topic.
Additionally, being a ‘fly on the wall’ enables us to observe the intricate dynamics of group communication and the interplay of diverse perspectives and opinions. This opportunity allows us to broaden our perspectives and question our beliefs as we engage with the diverse viewpoints shared in the discussion. Engaging deeply in the conversation allows us to grasp a fuller and richer understanding of the subject matter.
In the realm of gamification, listening to discussions on a topic can offer essential insights for crafting captivating and interactive experiences. By grasping the subtleties of how individuals discuss and interact with a subject, game developers can craft gameplay that is more immersive and meaningful. Incorporating real-life dialogue and scenarios into games can make them more authentic, relatable, and ultimately more enjoyable for players. Table 1 shows the instructions for the AI to be a fly on the wal, and the results generated by AI.
Table 1: The fly on the wall’ strategy to simulate a conversation about Eco-Serbia.

Phase 2 – Using Detailed Instructions to AI to Create the Game
To craft a game, the AI must produce questions that are both stimulating and demanding, while also being enjoyable and captivating for the players. Incorporating elements of surprise, humor, or suspense into the questions can achieve this, along with varying the difficulty level or topic to engage a diverse group of players. The goal is to craft an engaging and lively game experience that captivates players and encourages them to return for more excitement. Using the AI’s cognitive skills and computational strength, game developers can craft tailored and immersive gaming experiences that resonate with the varied preferences and interests of players. The aim is to use AI’s potential to enrich the gaming experience, crafting more interactive and enjoyable games into which players can immerse themselves (Table 2).
Table 2: The AI-simulated created of the Eco-Serbia project, showing the instruction to the AI, and the steps returned to create the game.

Phase 3 – ‘Harvesting and Answering Questions Generated by AI at the End of Iteration 1, as well as Questions Asked in Iteration 2, and Finally Questions Emerging When AI Reviewed the Material After the Study was Closed
AI in platforms like Idea Coach on BimiLeap.com consistently prompts relevant questions and when instructed answers to those questions. These questions highlight important issues related to the topic. Inserting these questions into a BimiLeap iteration is simple, regardless of the topic’s origin or relevance. The user directs the AI, through the Idea Coach feature, to respond to the question using Chat GPT3.5 in a format relevant to the user. Table 3 shows 25 questions and answers generated by AI and answered by AI. These 25 questions and answers may overlap, but in the interests of showing what can be learned, all questions and answers are included.
Table 3: AI generated questions about the topic, and AI generated answers to those questions.


Phase 3: AI as Teacher of Critical Thinking by Reviewing the Original AI Output Automatically After the Study is Closed for Further Iteration
What are the Key Ideas?
The key ideas generated by AI in a topic provide a concise summary of the main concepts and themes within the subject matter (Table 4). Knowing the key ideas allows students to quickly grasp the most important information, enabling them to better understand and absorb the material. To find these key ideas, students can use tools such as text analysis software or utilize critical thinking skills to identify recurring themes and main points. Once the key ideas are determined, the next steps involve further exploring and analyzing them to deepen comprehension and stimulate critical thinking.
Table 4: Key Ideas
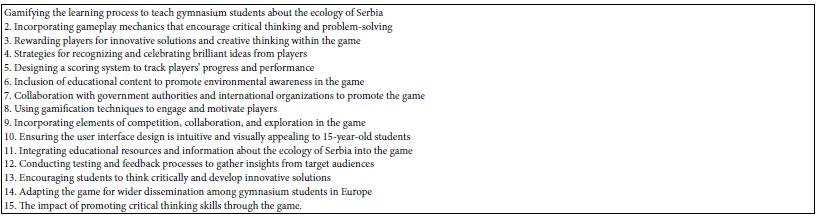
Finding key ideas and utilizing them to teach critical thinking is essential for developing students’ analytical skills and ability to extract meaningful information from complex topics. By focusing on key ideas, students learn to identify the most important elements of a subject and distinguish between relevant and irrelevant information. This process encourages critical thinking by prompting students to evaluate, question, and form their own opinions based on the key concepts presented.
What are the Themes and How do These Themes Manifest Themselves as Perspectives?
By exploring the themes highlighted by AI in the Mind Genomics analysis, individuals uncover a richer understanding of the patterns and foundational concepts embedded in the data. Examining the expression and interconnection of these themes allows researchers to glean valuable insights and pinpoint key takeaways from the study. A young researcher in Serbia can gain fresh insights and inspiration by exploring the list of themes, enriching their grasp of the subject matter. Through the examination of themes, students enhance their critical thinking abilities, recognizing patterns, forging connections, and deriving conclusions from the presented data. This approach prompts students to engage in analytical thinking, evaluate information with a critical eye, and present well-reasoned arguments to back their conclusions. The list of themes can act as a springboard for further research, igniting curiosity and encouraging students to explore the subject matter more deeply.
Students can enhance their critical thinking skills by examining the underlying assumptions and implications of each theme in the list. They can investigate the links between various themes and reflect on how these elements enhance the overall comprehension of the subject. Students can assess the relevance of each theme, gauge its impact on the research findings, and pinpoint any gaps or inconsistencies that may arise.
The themes identified through AI analysis provide a useful resource for enhancing critical thinking skills in education. Through a thoughtful exploration of themes, students can sharpen their analytical skills, foster logical thinking, and empower themselves to make well-informed decisions. This approach deepens understanding of the subject while inspiring students to tackle research and problem-solving with critical and analytical thinking (Table 5).
Table 5: Key themes recurring in the material generated by AI about the Eco-Serbia project, and the emerging perspectives.

Interested Audiences versus are Opposing Audiences
Understanding the interested and opposing audiences for the Eco-Serbia project, along with its gamification element, can significantly enhance our efforts in multiple ways. Identifying the audience interested in the topic enables us to customize our messaging and strategies, ensuring we engage and educate them effectively. This understanding enables us to craft focused campaigns and initiatives that connect with our audience, fostering increased participation and support for the project. Recognizing opposing audiences allows us to foresee challenges and objections, empowering us to tackle them head-on and refine our strategy to reduce resistance.
Additionally, grasping the perspectives of both supportive and opposing audiences can enhance critical thinking skills for participants and stakeholders alike. Through the examination of various viewpoints and the recognition of possible conflicts, individuals are prompted to engage in critical thinking regarding the project and its consequences. This cultivates a deeper insight into the relevant issues and promotes engaging conversation and discussion. Engaging with diverse viewpoints and opposing arguments allows participants to sharpen their analytical skills and make informed decisions regarding the project.
Integrating AI to analyze interested and opposing audiences in the Eco-Serbia project can significantly boost the effectiveness of its gamification elements. By grasping the preferences and viewpoints of various audience segments, we can customize the gamification elements to resonate more effectively with their interests and motivations. This focused method increases engagement and participation, paving the way for a more effective gamification strategy. By examining opposing viewpoints, we uncover potential challenges or concerns in the gamification process and tackle them proactively, creating a smoother and more enjoyable experience for all participants
Overall, it is important to address these potential oppositions by promoting the benefits of critical thinking, problem-solving, and environmental awareness, and by emphasizing the positive impact that the game can have on students’ education and understanding of the world around them (Table 6).
Table 6: Interested versus opposing audiences

Suggested Innovations – Analysis of Each from the Viewpoints and Business Opportunity, Respectively
The AI analysis prompts individuals to critically evaluate the project’s business dimensions. These dimensions include social aspects, uniqueness as well as business-case aspects. AI encourages individuals to foresee and tackle possible criticisms from investors, competitors, and other essential stakeholders, enabling researchers to craft a stronger and more convincing case for the gamification of the Eco-Serbia project. This thorough examination not only guides decision-making but also sharpens individuals’ capacity to strategically maneuver through intricate and layered challenges, ultimately boosting their critical thinking abilities along the way.
AI encourages individuals to question assumptions, challenge prevailing beliefs, explore alternative perspectives, and engage in strategic decision-making. The result is a culture of innovation, collaboration, and sustainability, crucial for tackling complex environmental challenges. Through critical analysis and reflection, individuals can cultivate stronger, more effective, and sustainable solutions for the Eco-Serbia project and beyond (Table 7).
Table 7: Deep AI analysis of four AI-suggested innovations.



Discussion and Conclusions
Making intellectual topics into games has greatly improved critical thinking by letting people interact with and think about knowledge in a fun and engaging way. Adding game features like challenges, puzzles, and competition encourages people to think critically and solve problems in order to win the game. This process helps people become better at analyzing things and pushes them to look at complicated issues from different points of view and think differently.
Gamification lets people use their critical thinking skills in the real world, making it easier to learn about and understand complicated topics through hands-on activities. People can improve their critical thinking skills in a safe and controlled setting by putting decision-making, strategy-building, and information processing into games. This makes them better at critical thought and gets them ready to use these skills in school, work, and personal life.
Using gamification as a tool helps people think more critically and interact with and learn more about intellectual topics in a more interesting and engaging way. This method turns learning into something fun and satisfying, which helps people understand and appreciate difficult topics more. By turning intellectual topics into games, people can connect with information in a fun and active way. This encourages exploration, analysis, and questioning, which leads to a deeper and more complete learning experience.
Adding game elements to educational topics could change the way people learn and improve their ability to think critically. Adding game features to intellectual and educational settings makes it easier for people to interact with and learn more about difficult topics in a fun and active way. This not only improves their critical thinking, but it also gives them the tools they need to deal with problems, face difficulties, and think deeply about different situations. By turning intellectual topics into games, people can start an interesting and exciting learning journey that can change them.
Acknowledgment
The authors gratefully acknowledge the ongoing help of Vanessa M Arcenas in the preparation of this manuscripts of the others in this grouping.
References
- Al-Menshawi A.H., Abu Al-Yazeed S (2020) Developing Skills of Systemic Thinking for Secondary Students. International Journal of Instructional Technology and Educational Studies, 1(2): 1-3.
- Gero A (2023) Systems thinking of secondary and post-secondary students majoring in engineering. Global Journal of Engineering Education, 25(3).
- Hernthaisong P, Sitti S, Sonsupap K (2015) Curriculum development for enhancing grade nine students systems thinking. Educational Research and Reviews, 10(12): 1722-1730.
- Rose J (2012) Application of systems thinking skills by 11th grade students in relation to age, gender, type of gymnasium, fluently spoken languages and international peer contact (Magister thesis) Wien: Universität Wien.
- Danry V.M (2023) AI enhanced reasoning: Augmenting human critical thinking with AI systems (Doctoral dissertation, Massachusetts Institute of Technology).
- Park C.S.Y, Kım H, Lee S (2021) Do less teaching, do more coaching: toward critical thinking for ethical applications of artificial intelligence. Journal of Learning and Teaching in Digital Age, 6(2): 97-100.
- Spector J.M, Ma S (2019) Inquiry and critical thinking skills for the next generation: from artificial intelligence back to human intelligence. Smart Learning Environments, 6(1): 1-11.
- Walter Y (2024) Embracing the future of Artificial Intelligence in the classroom: the relevance of AI literacy, prompt engineering, and critical thinking in modern education. International Journal of Educational Technology in Higher Education, 21(1), p.15.
- Yusuf A, Bello S, Pervin N, Tukur A.K (2024) Implementing a proposed framework for enhancing critical thinking skills in synthesizing AI-generated texts. Thinking Skills and Creativity, 53, p.101619.
- Joo T.M, Seng W.Y (2021) Validating the effectiveness of game-based learning approach in the form of video game for assessing computational thinking. Journal of ICT in Education, 8(4): 1-12.
- Lathifah A, Asrowi A, Efendi A (2023) Students’ Perspectives on Game-Based Learning and Computational Thinking. International Journal of Information and Education Technology, 13(3): 597-603.
- Shavab O.A.K, Yulifar L.E.L.I, Supriatna N.A.N.A, Mulyana A.G.U.S (2023) Development of gamification apps to enhance critical thinking and creative thinking. Eng. Sci. Technol, 18: 99-106.
- Zaibon Syamsul Bahrin, Emram Yunus. (2022) The effectiveness of game-based learning application integrated with computational thinking concept for improving student’s problem-solving skills. e-Infrastructure and e-Services for Developing Countries: 429-442.
- Bunt B, Gouws G (2020) Using an artificial life simulation to enhance reflective critical thinking among student teachers. Smart Learning Environments, 7(12).
- Katual D, Drevin L, Goede R (2023) GAME-BASED LEARNING TO IMPROVE CRITICAL THINKING AND KNOWLEDGE SHARING: LITERATURE REVIEW. Journal of the International Society for the Systems Sciences, 67.
- Muthmainnah, Ibna Seraj P.M, Oteir I (2022) Playing with AI to Investigate Human‐Computer Interaction Technology and Improving Critical Thinking Skills to Pursue 21st Century Age. Education Research International, 2022(1).
- Yang Y.T.C (2012) Building virtual cities, inspiring intelligent citizens: Digital games for developing students’ problem solving and learning motivation. Computers & Education, 59(2).